Forex & CFD contracts are leveraged to enable trading on margin. The amount of initial margin required to place a new trade is often only a small percentage of the total contract value. As leveraging provides traders with the ability to utilise a small amount of capital to control a large amount of assets, traders need to understand the concept of leveraged trading and the risks associated with it.
In this article, we aim to provide a clear explanation on the concept of margin trading and some popular terms you need to be aware of.
Initial Margin:
Amount required as a deposit when initiating a position.
Maintenance Margin:
Minimum amount that your account must maintain after initiating your position/s. A margin call will occur when your equity falls below this maintenance margin when your position is held overnight. On Phillip MT5, initial margin = maintenance margin.
Balance:
Balance shows the amount of deposited money in your trading account. The profit/loss of your orders will be added or deducted to/from your trading account balance when you close your orders. Do note that Balance reflects the realised value of your account.
Do note that Balance reflects the realised value of your account.
Equity:
Balance and Equity show the same values as long as there is not any open order. When you have open orders in your trading account, the Balance will not change and it will stay fixed but the Equity will float according to the profit/loss of your current orders. The formula is:
Equity = Balance + Profit & Loss
Margin:
Margin is the amount of the money that is used to open a position or trade and it is calculated based on the leverage. In other words it is the amount of the money that gets involved in a position as collateral. This money is locked until the position is closed. The formula is:
Margin = (Price symbol x Volume) / Leverage
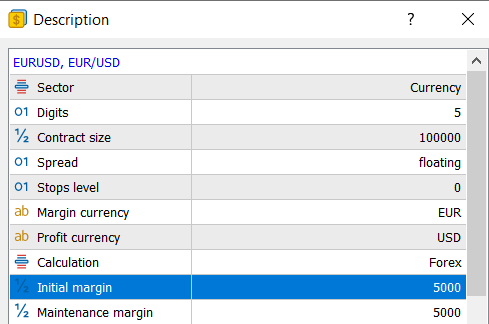
On MetaTrader 5, you are able to view the notional amount of initial margin for each contract under contract specifications.
Free margin:
Free margin is the difference of your account equity and margin used for the open positions. When you have no positions then no money from your account is used for margin. Therefore, all the money you have in your account is free. The formula is:
Free Margin= Equity – Margin
Margin level:
Margin level is the ratio of the equity to the margin. Margin level is very important since brokers use it to determine whether the traders can take any new positions when they already have some positions. Different brokers have different limits for the margin level, but this limit is usually 100% with most of the brokers. This limit is called Margin Call Level. The formula is:
Margin Level %= (Equity / Margin) x 100
Margin Call Level:
100% margin call level means if your account margin level reaches 100%, you can still close your open positions, but you cannot take any new positions. Indeed, 100% margin call level happens when your account equity, equals the required margin.
Stop Out Level:
For example, when the stop out level is set to 20% by a broker, the system starts closing your losing positions automatically if your margin level reaches 20%. It starts closing from the biggest losing position first. Usually, closing one losing position will take the margin level higher than 20%, because it will release the required margin of that position, and so, the total used margin will go lower and therefore the margin level will go higher.
The reason why this limit is setup is that the broker cannot allow you to lose more than the money you have deposited in your account.
Graphic illustration of margin:
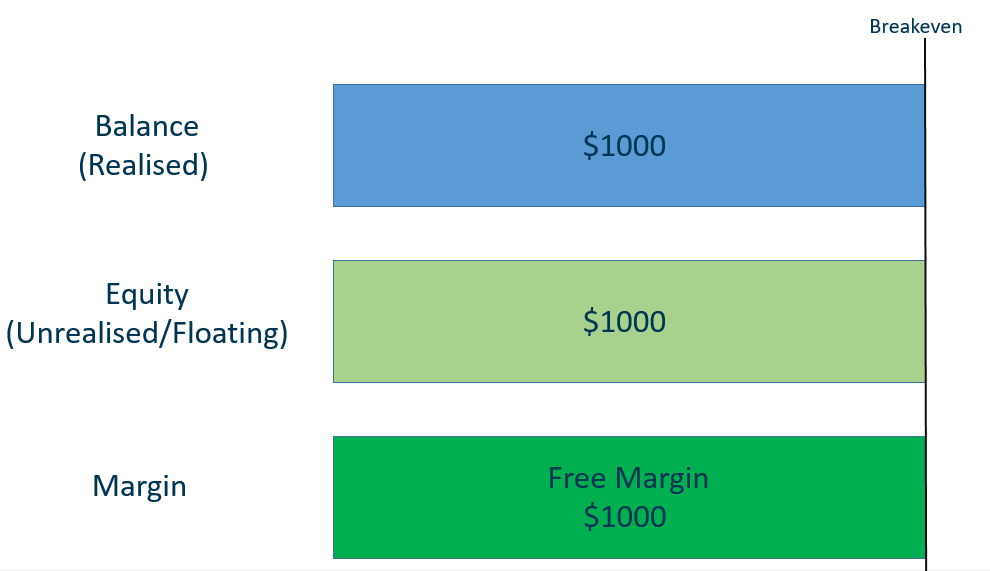
Suppose you have just deposited $1000 into your Phillip MT5 account. The balance and equity will be the same, at $1000 because there are no open positions. Free margin will also be $1000.
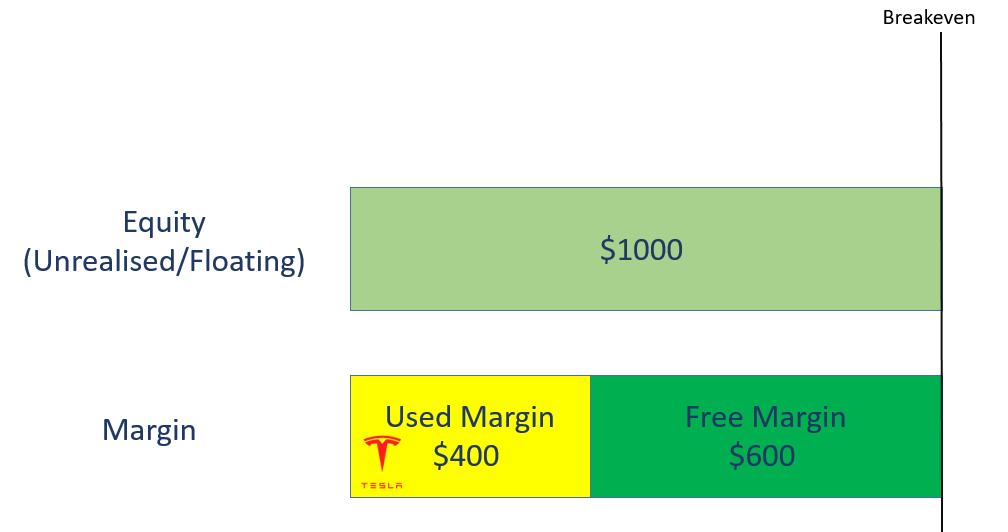
You long 2 Tesla share CFD @ $1000/share.
Your Position size will be calculated as $1000 x 2 = $2000.
The initial margin required for this position is $2000 x 20% margin = $400.
Assuming prices remain the same, equity level will maintain.
As $400 margin is used for the position, only $600 of free margin is available in your account.
If Tesla share CFD price rises from $1000 to $1250, your current position size = $1250 x 2 = $2500.
Compared to your initial position size of $2000, you have made an unrealised profit of $500, which is reflected on your equity.
Free margin also expands from $600 to $1100.
Do note that at this point, your balance is still $1000 because the $500 profit has not been realised.
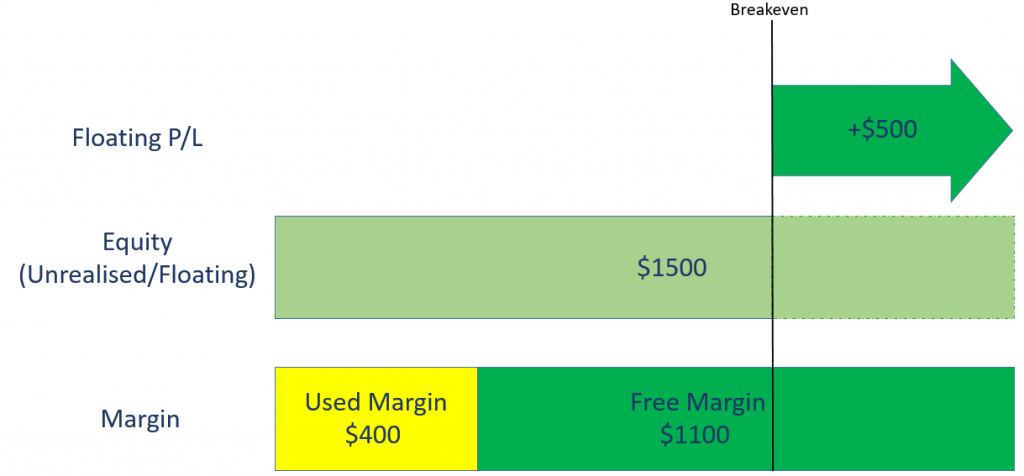
If Tesla share CFD price falls from $1000 to $750, your current position size = $750 x 2 = $1500.
Compared to your initial position size of $2000, you have made an unrealised loss of $500, which is reflected on your equity.
Free margin also reduces from $600 to $100.
Do note that at this point, your balance is still $1000 because the $500 loss has not been realised.
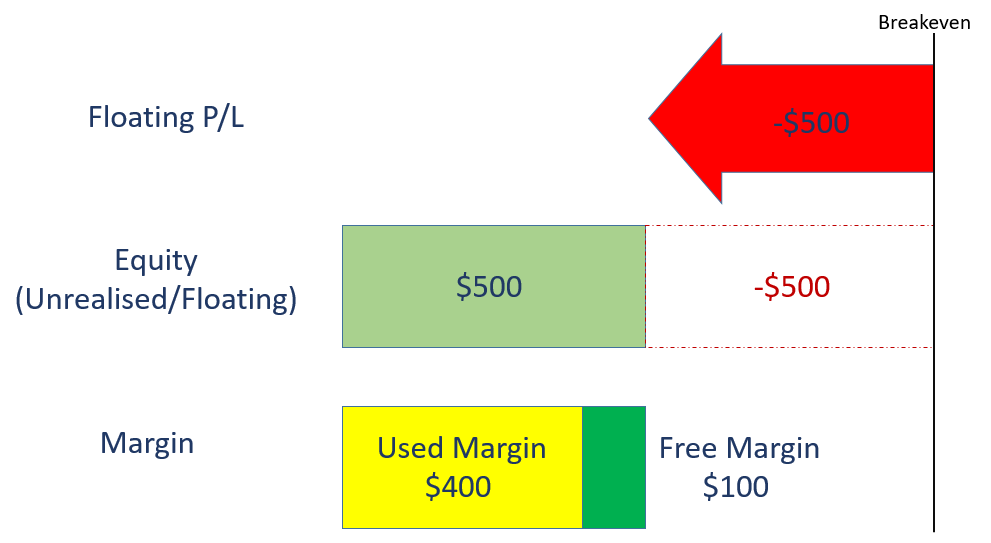
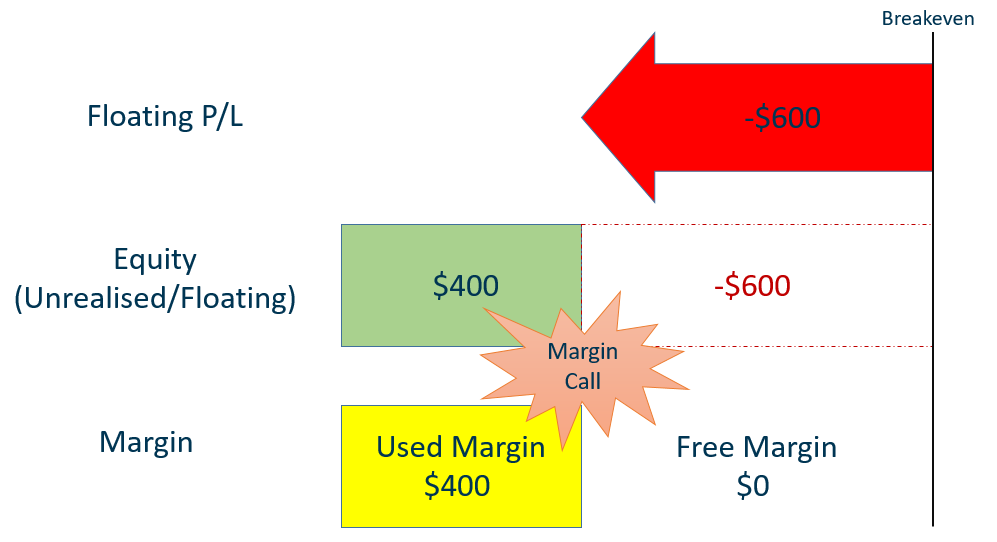
If Tesla share CFD price falls from $1000 to $700, your current position size = $700 x 2 = $1400.
Compared to your initial position size of $2000, you have made an unrealised loss of $600, resulting in $0 free margin.
According to Phillip Nova’s margin requirement policy, the maintenance margin = initial margin, you will receive a margin call as your margin = initial margin for your position ($400).
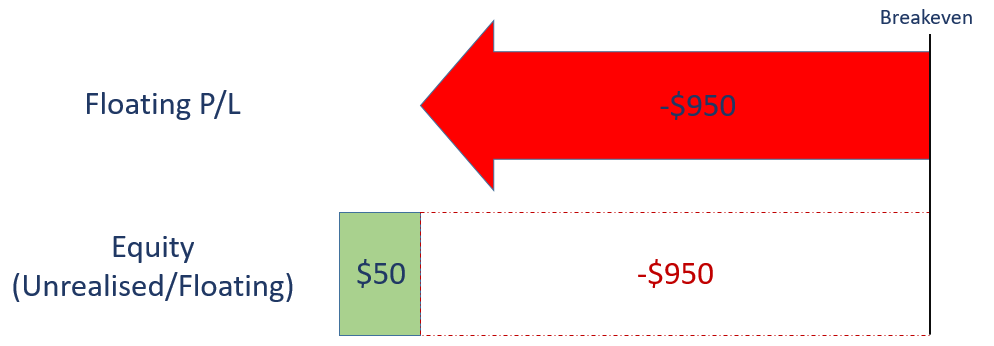
If Tesla share CFD price falls from $1000 to $525, your current position size = $525 x 2 = $1050.
Forced liquidation/auto cut is triggered, as your equity is now less than 20% of initial margin ($400).
Forced liquidation level = 20% X $400 = $80
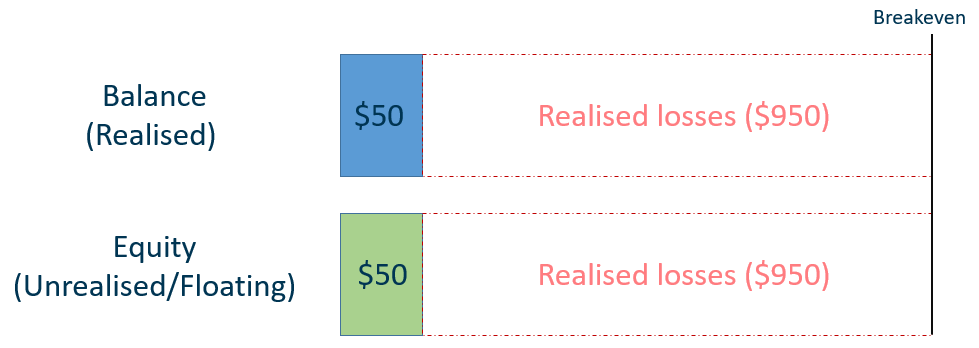
Your equity at $50 is below the forced liquidation level at $80.
Therefore, position will be auto cut and losses will be realised.
After the forced liquidation, losses will be realised.
Note: Forced liquated may not be executed at the best price, final balance may end up lower than 20% of IM.